Visual C++ - Send email using Gmail/G Suite OAuth 2.0 in background service (service account)¶
By default, you need to enable ” Allowing less secure apps” in Gmail/G Suite/Google Workspace, then you can send email with user/password SMTP authentication.
However Google will disable traditional user authentication in the future, switching to Google OAuth is strongly recommended now.
Sections:
- Installation
- Add reference
- Google Service Account
- Create project in Google Developers Console
- Create service account in current project
- Create service key
- Enable Gmail API
- Authorize service account by G Suite administrator
- Enable TLS Strong Encryption Algorithms in .NET 2.0 and .NET 4.0
- Access token lifetime
- Visual C++ - Send email using Gmail/G Suite OAuth 2.0 with service account - example
- EA Oauth Service for Gmail
- TLS 1.2 protocol
- Related links
Installation¶
EASendMail is a SMTP component which supports all operations of SMTP/ESMTP protocols (RFC 821, RFC 822, RFC 2554). Before you can use the following example codes, you should download the EASendMail Installer and install it on your machine at first.
Add reference¶
To use EASendMail SMTP ActiveX Object in your C++ project, the first step is “Add
header files of EASendMail to your project”. Please go to C:\Program Files\EASendMail\Include\tlh
or C:\Program Files (x86)\EASendMail\Include\tlh folder,
find easendmailobj.tlh and easendmailobj.tli, and then copy these
files to your project folder.
Google Service Account¶
Normal OAuth requires user input user/password in Web Browser. Obviously, it is not suitable for background service. In this case, you should use google service account to access G Suite or Google Workspace email service without user interaction. Service account only works for G Suite or Google Workspace user, it doesn’t work for personal Gmail account.
Create project in Google Developers Console¶
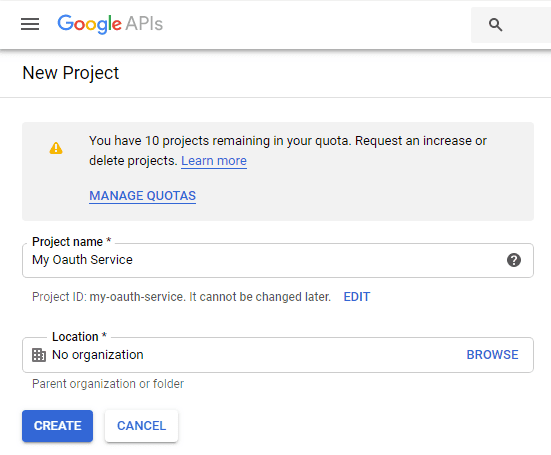
To use “G Suite or Google Workspace Service Account OAuth” in your application, you should create a project in Google Cloud Console at first.
Important
You can use any google user to create service account, it doesn’t require service account owner is a user in G Suite. But G Suite or Google Workspace administrator must authorize service account in Google Admin Console to access user mailbox.
Open Google Cloud console, create a new project by https://console.cloud.google.com/projectcreate.
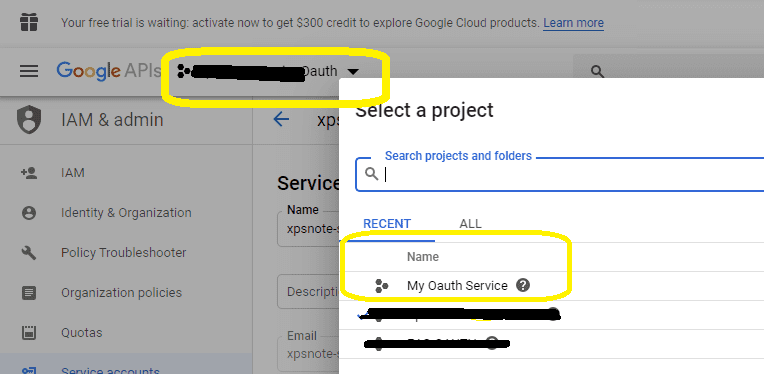
After the project is created, select it from projects list as current project.
Create service account in current project¶
Click
"Credentials"->"Manage service accounts"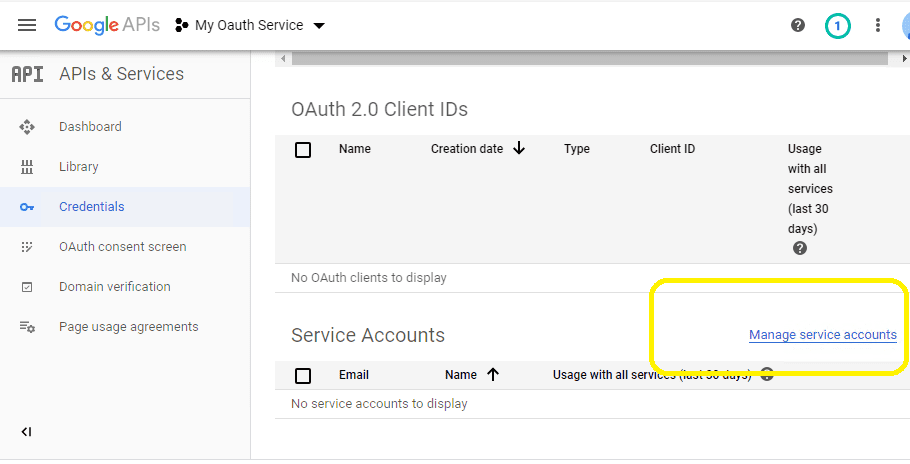
Click
"CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT"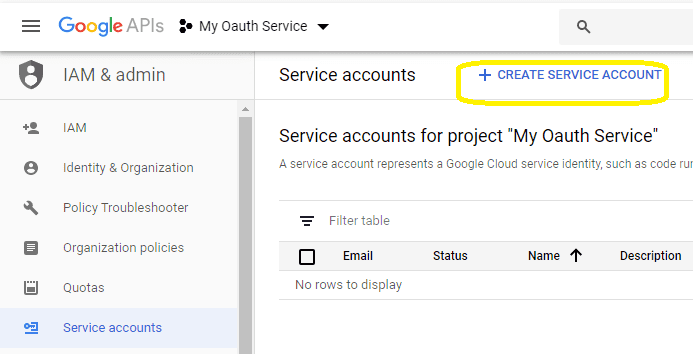
Input a name for your service account, click
"DONE"
After service account is created, you should enable "Domain-wide delegation" and create service key pair
to access G Suite or Google Workspace user mailbox.
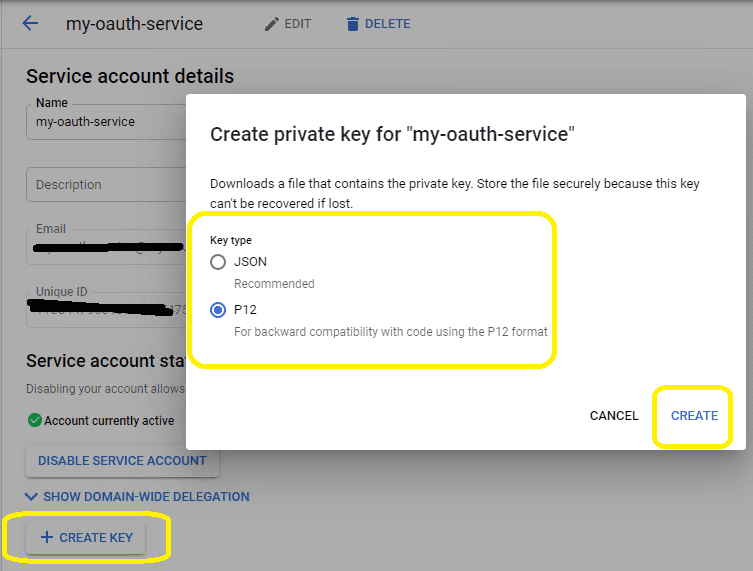
Create service key¶
Go back to your service account -> Keys, click
Add Key, you can select"p12"or"json"key type, both can work well, then you will get a file which contains private key, save the file to local disk.Now you have created service account with key pair successfully. You can use created private key in your codes to request
"access token"impersonating a user in G Suite or Google Workspace.
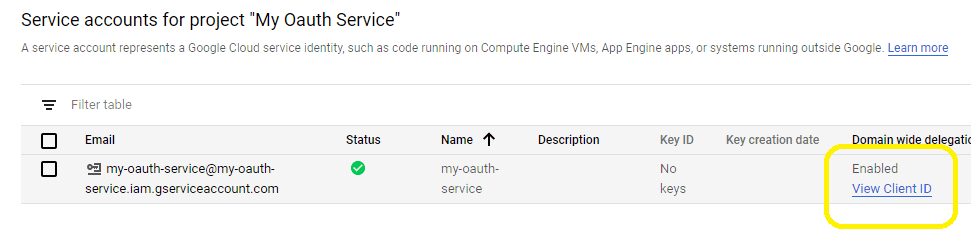
- To access user data in G Suite, you must get authorization from G Suite or Google Workspace administrator. You should go back to your service account -> Details, copy your service account email address and client id.
Enable Gmail API¶
Enable Gmail API in "Library" -> Search "Gmail", then click "Gmail API" and enable it.
If you use Gmail API protocol to send email, you should enable this API, if you use SMTP protocol, you don’t have to enable it.
Authorize service account by G Suite administrator¶
To use service account to access user mailbox in G Suite or Google Workspace, G Suite Administrator should authorize specified service account at first.
Important
Important Notice: You can use any google user to create service account, it doesn’t require service account owner is a user in G Suite or Google Workspace. But G Suite or Google Workspace administrator must authorize service account in G Suite or Google Workspace Admin Console to access user mailbox.
The administrator should open admin.google.com, go to Admin Console, click
"Security">API Control;
In the Domain wide delegation pane, select Manage Domain Wide Delegation.
Click Add new.
In the Client ID field, enter the service account’s Client ID
Click Add new and enter your service account client ID.
Enter the
client IDof the service account or OAuth2 client ID of the app.In the OAuth scopes (comma-delimited) field, enter the list of scopes that your application should be granted access to. and input
https://mail.google.com/,email,profilein One or More API Scopes, click"Authorize".
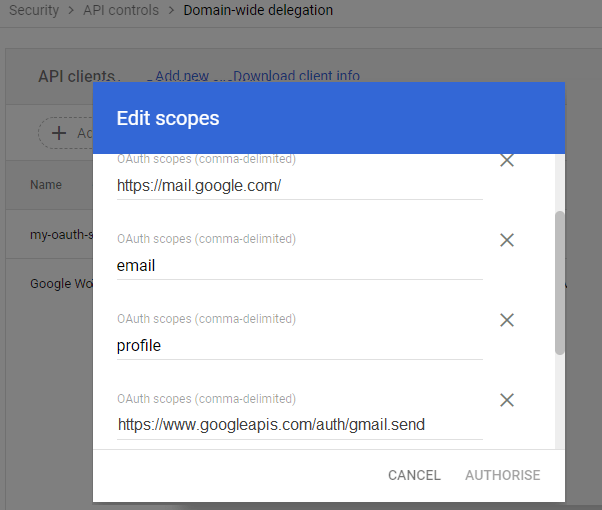
- Click Authorize.
After the administrator authorized service account, you can use it to access any users mailbox in G Suite or Google Workspace domain.
Learn more detail from: https://developers.google.com/identity/protocols/oauth2/service-account
Enable TLS Strong Encryption Algorithms in .NET 2.0 and .NET 4.0¶
Because HttpWebRequest is used to get access token from web service.
If you’re using .NET framework (.NET 2.0 - 3.5 and .NET 4.x),
you need to enable Strong Encryption Algorithms to request access token:
Put the following content to a file named NetStrongEncrypt.reg, right-click this file -> Merge -> Yes.
You can also download it from https://www.emailarchitect.net/webapp/download/NetStrongEncrypt.zip.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319]
"SystemDefaultTlsVersions"=dword:00000001
"SchUseStrongCrypto"=dword:00000001
Access token lifetime¶
You don’t have to request access token every time. By default,
access token expiration time is 3600 seconds, you can reuse the access token repeatedly before it is expired.
Visual C++ - Send email using Gmail/G Suite OAuth 2.0 with service account - example¶
#include "stdafx.h" // pre-compile header
#include "C:\Program Files (x86)\EASendMail\Include\tlh\EASendMailObj.tlh"
using namespace EASendMailObjLib;
#include "C:\Program Files (x86)\EASendMail\Include\tlh\msxml3.tlh"
using namespace MSXML2;
const int ConnectNormal = 0;
const int ConnectSSLAuto = 1;
const int ConnectSTARTTLS = 2;
const int ConnectDirectSSL = 3;
const int ConnectTryTLS = 4;
const int AuthAuto = -1;
const int AuthLogin = 0;
const int AuthNtlm = 1;
const int AuthCramMd5 = 2;
const int AuthPlain = 3;
const int AuthMsn = 4;
const int AuthXoauth2 = 5;
BOOL RequestAccessToken(const TCHAR* requestData, _bstr_t &accessToken)
{
try
{
IServerXMLHTTPRequestPtr httpRequest = NULL;
httpRequest.CreateInstance(__uuidof(MSXML2::ServerXMLHTTP));
if (httpRequest == NULL)
{
printf("Failed to create XML HTTP Object, please make sure you install MSXML 3.0 on your machine.\r\n");
return FALSE;
}
_bstr_t fullRequest = _bstr_t("grant_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Agrant-type%3Ajwt-bearer&assertion=") + requestData;
const char* postData = (const char*)fullRequest;
LONG cdata = strlen(postData);
LPSAFEARRAY psaHunk = ::SafeArrayCreateVectorEx(VT_UI1, 0, cdata, NULL);
for (LONG k = 0; k < (int)cdata; k++)
{
BYTE ch = (BYTE)postData[k];
::SafeArrayPutElement(psaHunk, &k, &ch);
}
_variant_t requestBuffer;
requestBuffer.vt = (VT_ARRAY | VT_UI1);
requestBuffer.parray = psaHunk;
_variant_t async(true);
_bstr_t uri("https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token");
httpRequest->setOption((MSXML2::SERVERXMLHTTP_OPTION)2, 13056);
httpRequest->open(L"POST", uri, async, vtMissing, vtMissing);
httpRequest->setRequestHeader(L"Content-Type", L"application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
httpRequest->send(requestBuffer);
while (httpRequest->readyState != 4) {
httpRequest->waitForResponse(1);
}
long status = httpRequest->status;
_bstr_t responseText = httpRequest->responseText;
if (status < 200 || status >= 300)
{
printf("Failed to get access token from server: %d %s\r\n", status, (const char*)responseText);
return FALSE;
}
IOAuthResponseParserPtr oauthParser = NULL;
oauthParser.CreateInstance(__uuidof(EASendMailObjLib::OAuthResponseParser));
oauthParser->Load(responseText);
accessToken = oauthParser->AccessToken;
if (accessToken.length() == 0)
{
printf("Failed to parse access token from server response: %d %s\r\n", status, (const char*)responseText);
return FALSE;
}
return TRUE;
}
catch (_com_error &ep)
{
printf("Failed to get access token: %s", (const char*)ep.Description());
return FALSE;
}
}
BOOL GenerateRequestData(const char* gsuiteUser, _bstr_t &requestData)
{
// service account email address
// You should create your client id and client secret,
const char* serviceAccount = "xxxx@xxxx.iam.gserviceaccount.com";
const char* scope = "https://mail.google.com/";
const char* aud = "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token";
ISimpleJsonParserPtr jwtPtr = NULL;
jwtPtr.CreateInstance(__uuidof(EASendMailObjLib::SimpleJsonParser));
_bstr_t header = jwtPtr->JwtBase64UrlEncode(_bstr_t("{\"alg\":\"RS256\",\"typ\":\"JWT\"}"));
// token request timestamp
long iat = jwtPtr->GetCurrentIAT();
// token expiration time
long exp = iat + 3600;
char iatBuf[MAX_PATH + 1];
char expBuf[MAX_PATH + 1];
sprintf_s(iatBuf, MAX_PATH, "%d", iat);
sprintf_s(expBuf, MAX_PATH, "%d", exp);
_bstr_t playload = _bstr_t("{");
playload += _bstr_t("\"iss\":\"") + _bstr_t(serviceAccount) + _bstr_t("\",");
playload += _bstr_t("\"scope\":\"") + _bstr_t(scope) + _bstr_t("\",");
playload += _bstr_t("\"aud\":\"") + _bstr_t(aud) + _bstr_t("\",");
playload += _bstr_t("\"exp\":") + _bstr_t(expBuf) + _bstr_t(",");
playload += _bstr_t("\"iat\":") + _bstr_t(iatBuf) + _bstr_t(",");
playload += _bstr_t("\"sub\":\"") + _bstr_t(gsuiteUser) + _bstr_t("\"");
playload += _bstr_t("}");
playload = jwtPtr->JwtBase64UrlEncode(playload);
ICertificatePtr cert = NULL;
cert.CreateInstance(__uuidof(EASendMailObjLib::Certificate));
// In web application, use CRYPT_MACHINE_KEYSET
if (cert->LoadPFXFromFile(_bstr_t("D:\\MyData\\oauth-77dac4d192ec.p12"),
_bstr_t("notasecret"), CRYPT_USER_KEYSET) == VARIANT_FALSE)
{
printf("Failed to load service account certificate!");
return FALSE;
}
_bstr_t signature = jwtPtr->SignRs256(cert, header + _bstr_t(".") + playload);
if (signature.length() == 0)
{
printf("Failed to sign request data!");
return FALSE;
}
requestData = header + _bstr_t(".") + playload + _bstr_t(".") + signature;
return TRUE;
}
void SendEmail()
{
::CoInitialize(NULL);
// gsuiteUser is the full email address of the user in GSuite, for example: user@gsuitedomain
const char* gsuiteUser = "user@mydomainingsuit.com";
_bstr_t requestData, accessToken;
if (!GenerateRequestData(gsuiteUser, requestData))
{
return;
}
// request access token from Google server by service account
// withou user interaction
if (!RequestAccessToken((const TCHAR*)requestData, accessToken))
{
return;
}
IMailPtr oSmtp = NULL;
oSmtp.CreateInstance(__uuidof(EASendMailObjLib::Mail));
oSmtp->LicenseCode = _bstr_t("TryIt");
// Gmail SMTP server address
oSmtp->ServerAddr = _bstr_t("smtp.gmail.com");
oSmtp->ServerPort = 587;
// Enable SSL/TLS connection
oSmtp->ConnectType = ConnectSSLAuto;
// Gmail OAUTH type
oSmtp->AuthType = AuthXoauth2;
oSmtp->UserName = _bstr_t(gsuiteUser);
oSmtp->Password = accessToken;
oSmtp->FromAddr = _bstr_t(gsuiteUser);
// Please change recipient address to yours for test
oSmtp->AddRecipient(_bstr_t("Support Team"),
_bstr_t("support@emailarchitect.net"), 0);
oSmtp->Subject = _bstr_t("Test email using G suite service account");
oSmtp->BodyText = _bstr_t("Hello, this is a test....");
if (oSmtp->SendMail() == 0)
printf("Message delivered!");
else
printf((const char*)oSmtp->GetLastErrDescription());
}
EA Oauth Service for Gmail¶
If your code is too complex or out of maintenance, and you don’t want to change anything in your source codes, then you can have a try with EA Oauth Service for Gmail. It provides an easy way for the legacy email application that doesn’t support OAUTH 2.0 to send and retrieve email from Gmail without changing any codes. SMTP, POP, IMAP and SSL/TLS protocols are supported.
TLS 1.2 protocol¶
TLS is the successor of SSL, more and more SMTP servers require TLS 1.2 encryption now.
If your operating system is Windows XP/Vista/Windows 7/Windows 2003/2008/2008 R2/2012/2012 R2, you need to
enable TLS 1.2 protocol in your operating system like this:
Enable TLS 1.2 on Windows XP/Vista/7/10/Windows 2008/2008 R2/2012
Appendix
- Send Email in Visual C++ - Tutorial
- EASendMail SMTP Component SDK
- Process Bounced Email (Non-Delivery Report) and Email Tracking
- Bulk Email Sender Guidelines
- Work with Email Queue
Comments
If you have any comments or questions about above example codes, please click here to add your comments.